|
The Obesity Epidemic
Obesity is a life-threatening disease afflicting the United States at an alarming rate. A quarter of the population is obese,and another 97 million Americans are overweight or at risk of becoming obese. The prevalence of obesity has increased more than 60% in the past decade. Given this aggressive increase in the rate of obesity, experts predict that this national health crisis will only continue to escalate.
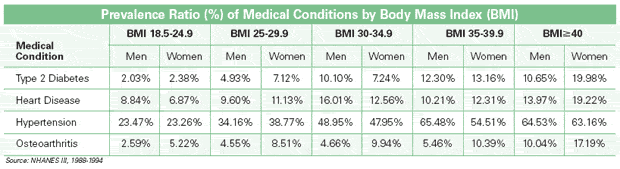
Contributing to 300,000 deaths each year,obesity is considered the second leading cause of preventable death after smoking. In fact, it is more damaging to your health than smoking and alcohol abuse. In addition, obesity is a major risk factor for serious medical conditions (co-morbidities), such as:
- type 2 diabetes
- hypertension
- heart disease
- stroke
- sleep apnea
- respiratory problems
- cancer
- osteoarthritis
- joint problems
The cost of this serious disease is enormous, with an estimated annual treatment cost in excess of $238 billion, of which roughly $100 billion is devoted to treating related health problems. Additionally, Americans spend $33 billion each year on weight-loss products and services.
Measuring Obesity
The most common measurement for obesity is the Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI is the body weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters (BMI = kg/m2). While BMI does not actually measure body fat, it tends to correlate well with the degree of obesity. Thus it should not be used alone for diagnosis, but can be useful as a general guideline.
The BMI calculation cannot distinguish between body fat and muscle. This could cause a very muscular person to be mistakenly classified as obese. For this reason, your physician should always consider your individual case.
The obesity categories adopted in 1998 by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are:
- BMI 25 to 29.9 kg/m2 ? Overweight BMI 30 to 34.9 kg/m2 ? Obese
- BMI 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 ? Severely Obesity
- BMI 40 kg/m2 and up ? Morbidly Obese
The Threat of Morbid Obesity
The Morbid Obesity category represents individuals who carry the largest and most dangerous amount of excess body weight.In simple terms, it is defined as:
- BMI >= 40 or
- Weighing at least twice the ideal weight or at least 100 pounds more than ideal weight
Morbid obesity greatly increases the chance of developing health conditions that can result in significant physical,mental and social disabilities. It can also cause death. Morbidly obese as well as severely obese individuals with a BMI of 35 or more with obesity-related health problems may be considered candidates for obesity surgery.
Obesity Causes
Obesity is not a sign that a person is out of control. Many things can lead to this chronic disease, such as:
- Energy balance - Taking too much energy from food that is in excess of what the body needs can lead to weight gain, depending on individual metabolism and activity level.
- Heredity - If others in your family are obese, you have a higher risk for obesity.
- Metabolic disorders ? Changes in metabolism, or how your body gets energy from food, may affect your energy balance and your weight.
- Eating and social habits - Eating an unbalanced diet, snacking between meals, and not getting enough exercise may all contribute to obesity.
- Psychological factors - Social or emotional eating is also one of the main causes of gaining excess weight.
Any one or a combination of these factor scan lead to obesity. As science continues to search for answers, morbidly obese individuals must understand how to treat their condition in the most effective way.
Next: Obesity Treatment Options >>
|

 email to a friend
email to a friend printer-friendly version
printer-friendly version
