Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) Weight Loss Procedure
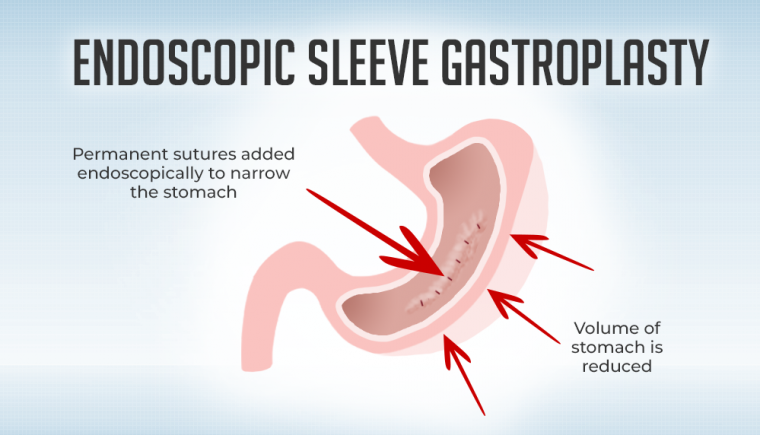
June 10, 2019Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is an incisionless weight loss procedure that is performed with an endoscope placed through the mouth and into the stomach. The procedure uses permanent sutures to narrow the stomach. The procedure takes about an hour and most patients are discharged home the same day, again without any incisions.
Studies have shown that weight loss is significant and seems to be persistent for several years.
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty is Less Invasive
Weight loss occurs due to the restriction caused by narrowing the stomach, and it has also been shown to affect hormones involved in hunger and satiety. Because the procedure is less invasive, it has a lower complication rate than the laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy but also has less weight loss.
The endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty has now been performed around the world thousands of times with consistent weight loss results. The procedure has shown to be best suited for those that may not qualify for weight loss surgery, such as those patients with a body mass index (BMI) in the 30-35 range and comorbid conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, or high cholesterol; 35-40 range, or sometimes greater than 40 if the patient is unable to have surgery due to extensive previous abdominal surgery for example.
Like any weight loss procedure, the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty does require a commitment to diet and exercise before and after the procedure. It may not be for everyone and thus it does require a physician trained in bariatrics to perform a screen to confirm eligibility.
Risks of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty
The most common risks of the procedure are nausea and pain immediately after the procedure. These typically resolve within one week. Studies have shown that complications occur in approximately 5% of patients which is three times less than common surgical weight loss procedures.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. A flexible camera is placed through the mouth and into the stomach. Approximately 8-12 sutures are then placed which narrows the stomach to about the size and shape of a typical banana, about one-third the original size. Most patients are discharged home after a short stay in the recovery room and ambulatory area.
Some patients are not candidates for this procedure such as those who have had previous surgery on organs such as the esophagus or stomach. Others with cirrhosis or bleeding problems may also not qualify. Different centers may have different contraindications for the procedure, so be sure to consult with the physician who performs the procedure.
Most centers that perform this procedure have a multidisciplinary team that aids in diet and exercise before and after the procedure. These are necessary for the results to be maintained lifelong.
Another common member of the multidisciplinary team is a bariatric psychologist. Psychologists not only help with weight loss but also in managing the psychological changes that occur after significant weight loss. Most patients must follow a liquid diet immediately after the procedure for a short duration but eventually return to a normal diet that is hopefully healthier and likely smaller portions. These diet regimens are typically learned from a dietician on the multidisciplinary team.
Results of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty
Studies to date have shown weight loss ranging from 40-75 pounds at one year, or 30-50% excess weight loss. Excess weight is calculated by subtracting the ideal weight from the current weight.
A study combining multiple centers from around the world showed that this weight loss persists for at least three years. More studies will be needed to show that the results persist as long as other weight loss surgeries.
As with other weight loss surgeries, the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty appears to also play a role in preventing or improving other diseases related to being overweight such as diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, high cholesterol, and osteoarthritis. There are minimal long-term side effects. One concern was that it could lead to worsening gastroesophageal reflux disease, however, studies have shown that the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty results in less gastroesophageal reflux than the laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy.
If the occasion were ever to arise to reverse the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, this can be performed. The sutures can be cut if needed and there are reports of patients undergoing surgical weight loss procedures after failing to lose adequate weight from the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty. If a patient undergoes an endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty and wants it reversed, it is highly recommended that a surgical endoscopist familiar with the procedure perform the reversal. It is, of course, rare to ever want a reversal.
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty Summary
In summary, the endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is an incisionless procedure that results in a narrowing of the stomach and significant weight loss through food restriction and less hunger. The procedure has a low complication rate and lesser recovery than surgical weight loss procedures but must be approached by the patient in much the same way as a surgical procedure in terms of following a good healthy diet with appropriate portions, and exercise.
 | ABOUT THE AUTHOR Michael B. Ujiki is an Advanced Laparoscopic & Bariatric Surgeon at NorthShore University HealthSystem Bariatric Center. Dr. Ujiki went to Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine in 2000 and had his internship at McGaw Medical Center of Northwestern University in 2001. Dr. Ujiki took up his residency at Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine; McGaw Medical Center of Northwestern University in 2007 and fellowship at Legacy Health System in 2008. Dr. Ujiki treats patients in a minimally invasive way so that recovery is faster. |



